Position: Resource - Disk Utilities - Convert to Dynamic Disk, Should I Make the Switch?
Dynamic disks have more advanced features than basic disks. They allow the creation of volumes that span multiple disks, such as spanned and striped volumes, and support fault-tolerant volumes, such as mirrored volumes and RAID-5 volumes. Dynamic disks use a database to track information about dynamic volumes on the disk and other dynamic disks in the computer, which is useful for repairing a corrupted database using information from another dynamic disk.
Dynamic disks are especially useful when you need to manage volumes across multiple physical disks because they provide greater flexibility for volume management.
Basic disks are the most commonly used disk type in Windows. They are characterized by simplicity and support for primary partitions, extended partitions, and logical drives. These partitions are usually formatted with a file system such as NTFS to create volumes for storing files. Basic disks are versatile and can adapt to a variety of storage requirements, making them suitable for a variety of situations. They support cluster disks, IEEE 1394 disks, and USB removable drives. Basic disks can use either the Master Boot Record (MBR) or GUID Partition Table (GPT) partition style, depending on the system's support.
One of the main operations that can be performed on a basic disk is to extend a volume to adjacent unallocated space on the same disk, provided that the disk has been formatted with the NTFS file system. This flexibility makes it easy to expand storage space without creating new volumes.
- Better disk management: Dynamic disks allow you to create, extend, or delete volumes without restarting the system, which is very convenient for users who need to frequently adjust disk configurations.
- Data redundancy and fault tolerance: Dynamic disks can provide higher data redundancy and fault tolerance by using mirrored volumes or RAID-5 volumes. If your data is very important, dynamic disks can provide an extra layer of protection for your data.
- Performance improvement: Spanned volumes can combine multiple physical disks into one logical volume, thereby increasing storage capacity and improving read and write performance. RAID-5 volumes provide higher read and write speeds and data redundancy through data striping and parity.
- Compatibility issues: Dynamic disks can only be used in Windows 2000 and later operating systems. If your computer is running multiple operating systems at the same time, especially non-Windows systems, converting to dynamic disks may cause some operating systems to fail to recognize the disk.
- Data risks: During the conversion process, the operating system will warn you that there may be a risk of data loss. Although data will not be lost in most cases, there is still a certain risk. It is recommended to back up all important data before conversion.
- Management complexity: Although dynamic disks provide more management options, operation and management may become more complicated for non-professional users. If you are not familiar with the management of dynamic disks, it may cause configuration errors or performance problems.
Whether you should convert a basic disk to a dynamic disk depends on your specific needs and usage scenarios. If you are an ordinary user, mainly for daily office and entertainment, a basic disk is sufficient to meet your needs. But if you are an enterprise user who needs higher performance and data protection, or needs to frequently adjust the disk configuration, a dynamic disk may be a better choice.
- Backup data: Before converting, be sure to back up all important data just in case.
- Test environment: If conditions permit, you can convert in a test environment to familiarize yourself with the operation and management methods.
- Consult professionals: If you are not sure how to operate, it is recommended to consult professional technicians.
1. Open the "Disk Management" tool (you can access it by right-clicking "This PC" -> "Manage" -> "Disk Management").
2. Find the basic disk you want to convert and right-click the number of the disk (for example, "Disk 1").
3. Select "Convert to Dynamic Disk".

4. Follow the wizard prompts to complete the conversion.


Note: It is recommended to back up important data before performing any disk operations.
Step 1. Open the command prompt as an administrator.
Step 2. Enter diskpart and press Enter.
Step 3. Enter list disk to view all disks and find the disk number that needs to be converted.
Step 4. Enter select disk X (X is the disk number to be converted).
Step 5. Enter convert dynamic to convert.

Step 6. Enter exit to exit diskpart.
Dynamic disks may cause compatibility issues in some cases, especially when replacing hardware or system, so sometimes users may need to convert dynamic disks to basic disks. Or some users may accidentally convert a disk to dynamic disk in Windows and want to convert the dynamic disk back to basic disk without losing data. In the above situation, you can use the professional conversion tool DiskGenius, which can help you convert dynamic disks to basic disks without losing data. In addition, DiskGenius can also help you manage dynamic disk partitions.
Follow the simple steps below to convert a dynamic disk to basic disk:
Step 1. Visit the official website of DiskGenius (www.diskgenius.com) and download the latest version. Run the downloaded installer and follow the prompts to complete the installation.
Step 2. Double-click the DiskGenius icon on the desktop to start the program. After the program starts, the left window will display all connected disks and partitions. Select the dynamic disk to be converted and select "Disk" - "Convert To Basic Disk".
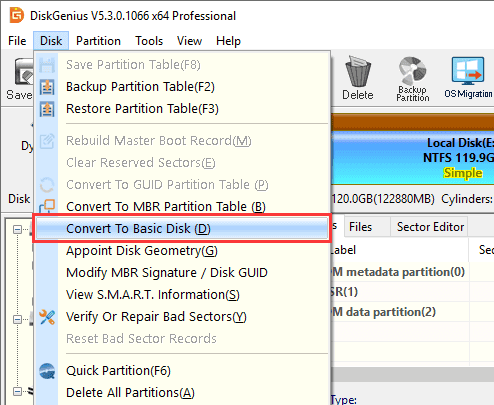
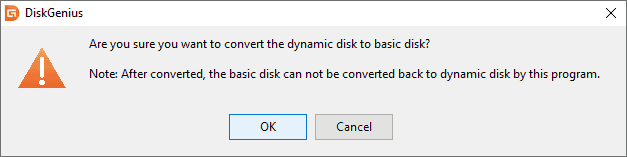
Step 3. Click the OK button to confirm your choice.
Note: After conversion, the program cannot convert the disk to a dynamic disk.
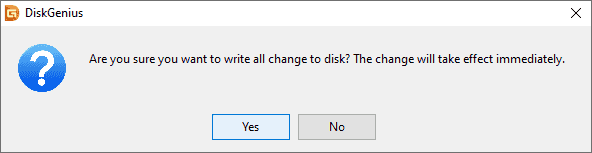
Step 4. Click Save All on the toolbar, and then click Yes to save the changes to disk.
Q 1: What are the differences between basic disks and dynamic disks?
A: Basic disks and dynamic disks are two different disk management methods in the Windows operating system. They have obvious differences in partition types, management functions, and applicable scenarios. The following are their main differences:
1. Partition Type
Basic disk:
- Supports primary partitions, extended partitions, and logical drives.
- Each disk can have up to four primary partitions, or three primary partitions plus one extended partition. Extended partitions can contain multiple logical drives.
Dynamic disk:
- Supports multiple types of volumes, including simple volumes, spanned volumes, striped volumes, mirrored volumes, and RAID-5 volumes.
- Volumes can span multiple physical disks, providing more flexible storage management.
2. Disk Management Functions
Basic Disk:
- Provides basic partition management functions, such as deleting, formatting, and creating partitions.
- Does not support dynamic expansion or reduction of partition size, nor does it support partitions across multiple disks.
Dynamic Disk:
- Provides more advanced disk management functions, such as extending volumes, creating striped volumes, and mirrored volumes.
- Supports dynamic expansion and reduction of volume size, and creation of volumes across multiple disks.
- Supports RAID technology, providing data redundancy and performance optimization.
3. RAID Support
Basic Disk:
- Does not support RAID technology.
Dynamic Disk:
- Supports multiple RAID configurations, such as RAID-0 (striped volume), RAID-1 (mirrored volume), and RAID-5 volumes, providing data redundancy and performance improvement.
4. Applicable Scenarios
Basic disk:
- Suitable for individual users and small businesses, especially in the case of single disk and simple partition requirements.
Dynamic disk:
- Suitable for enterprises and advanced users who need advanced disk management functions, especially in the scenario of data redundancy, performance optimization and flexible storage management.
5. Data Security
Basic disk:
- Generally lacks redundancy and fault tolerance, and the risk of data loss is relatively high.
Dynamic disk:
- Supports mirrored volumes (RAID-1), which can effectively prevent data loss and provide data redundancy. If one disk fails, the data can still be accessed through another disk.
6. Compatibility Issues
Basic disk:
- Can be easily transferred and used between different Windows operating systems.
Dynamic disk:
- Although many versions of Windows support dynamic disks, dynamic disks may not be recognized in some older versions or non-Windows systems.
Q 2: Which disk type should I use?
A: If your usage requirements are simple, such as installing an operating system and general file storage, a basic disk is sufficient. If you need more complex management functions, or need performance and data redundancy, you should choose a dynamic disk.
Q 3: Do dynamic disks affect performance?
A: For configurations such as striped volumes, dynamic disks can improve performance, but the complexity also increases accordingly. If the disk failure rate is high, it may affect the stability and performance of the entire system in a RAID configuration.
Q 4: Can I use basic disks and dynamic disks together?
A: Yes, Windows supports the use of basic disks and dynamic disks in the same system at the same time. Users can choose the appropriate disk type according to different needs.
Converting a basic disk to a dynamic disk is a relatively simple process, but there are some key steps and potential risks to be aware of. By following the steps above, you can successfully complete the conversion and take advantage of the additional management options and performance improvements provided by dynamic disks. Hopefully, this article will help you better understand the difference between basic disks and dynamic disks, and whether you should convert a basic disk to a dynamic disk. If you run into any issues during the process, or need further assistance, please feel free to contact us.

DiskGenius is a one-stop solution to recover lost data, manage partitions, and back up data in Windows.
Download