Position: Resource - Disk Utilities - Fixed: IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL Stop Code in Windows 11/10/8/7
"Your device ran into a problem and needs to restart. We're just collecting some error info, and then we'll restart for you.
90% complete
For more information about this issue and possible fixes, visit https://www.windows.com/stopcode
If you call a support person, give them this info:
Stop code: IRQL NOT LESS OR EQUAL"

In computing, IRQL stands for "Interrupt Request Level". It is a priority level assigned to each device connected to a computer system that determines how much priority the device has to access system resources. The higher the IRQL level, the more priority a device has to perform its tasks. IRQL is used by the operating system to manage and prioritize system resources and to prevent conflicts between different devices and drivers.
In the context of a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) error message, the IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL is a common error message that appears on Windows operating systems when there is a problem with the computer's memory or drivers. The BSOD error message indicates that a process or driver attempted to access a memory address at a higher interrupt request level (IRQL) than it was allowed to, which can trigger a Windows blue screen crash or unexpected syste shutdown.
The causes of the IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error can vary, but some of the most common reasons include outdated or incompatible drivers, faulty hardware, and corrupt system files. In some cases, the error may be caused by a virus or malware infection. The most common ones are:
These are just some of the possible causes of the IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error. If you are experiencing this error, you can try solutions provided in this article to fix the issue.
IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL is a common Blue Screen of Death error (also known as a BSOD or stop code error) that usually occurs due to driver conflicts, faulty RAM, damaged hardware, or corrupted system files. It may cause your Windows system to crash, freeze, or automatically reboot after the blue screen appears. Here are some methods you can try to fix this error:
Tip: Before trying following solutions, be sure to take a moment to back up important files before making any system changes. Fixing BSOD issues can sometimes involve resetting drivers, running scans, or even restoring the system — any of which might risk your data if something goes wrong.
The following 11 solutions are listed from simple to complex. We start with easy fixes like restarting your PC and updating drivers, then move on to checking hardware and advanced settings. This order helps you solve the problem quickly and safely, avoiding unnecessary risks or effort.
The first step to take is to restart your computer. This may fix the error, especially if it's a temporary issue. So, if you haven't restarted your computer already, go ahead and do so to see if the error persists.

Outdated system files can cause the IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error. To fix this issue, check for any available Windows updates and install them. Here's how:
Step 1. Press the Windows key + I to open the Settings app.
Step 2. Click on "Update & Security" and then click "Check for updates".
Step 3. Install any available updates.
Excessive heat can make hardware parts, especially the CPU and GPU, stop working. This can generate IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL and other stop code issues. Keeping your PC cool helps keep the system stable.
How to keep your system cool:
- Clean your fans and vents. Dust can build up and obstruct ventilation, which can make things too hot.
- If your CPU is old or the temps seem too high, put thermal paste back on.
- Make sure the case has good airflow by organizing the wires and making sure the intake and exhaust fans are operating.
- If you're using a laptop, you should use a cooling pad.
- Don't use the PC for long amounts of time in a hot room or while it's really busy.
- You can use monitoring software like HWMonitor or Core Temp to check the temperatures within your computer.
A clean boot might help you figure out if third-party services or startup programs are generating system conflicts that lead to blue screen issues. It launches Windows with only the most important drivers and background programs.
Step 1. Press Windows + R, type msconfig, and then hit Enter.
Step 2. In the System Configuration box, click on the Services tab.
Step 3. Put a check in the box Hide all Microsoft services, and then click "Disable all".

Step 4. Go to the Startup tab and click on Task Manager. Turn off all startup items in Task Manager.
Step 5. Click OK in the System Configuration window and then close Task Manager. Reboot your computer.
Can RAM cause blue screen? Yes, RAM (Random Access Memory) can cause a blue screen error, also known as a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) in Windows. The BSOD error message can indicate a variety of errors related to memory, such as "MEMORY_MANAGEMENT" or "PAGE_FAULT_IN_NONPAGED_AREA", which are commonly caused by faulty or incompatible RAM. If your computer is experiencing frequent BSOD errors, it is possible that one or more of the RAM modules are faulty or have compatibility issues with your system.
On this occasion, you can run hardware diagnostics to check for any issues with your RAM, hard drives, or other components. To run hardware diagnostics, you can use the built-in Windows Memory Diagnostic tool or a third-party tool like MemTest86.
Step 1. To run the Windows Memory Diagnostic tool, press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
Step 2. Type "mdsched.exe" (without quotes) and press Enter.
Step 3. Click "Restart now and check for problems".
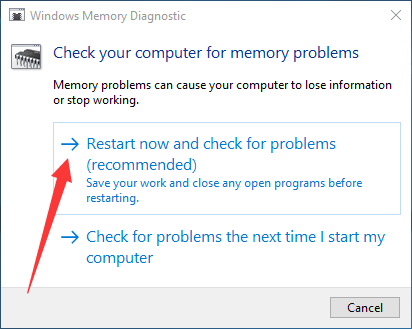
Step 4. Wait for the scan to complete.
Outdated or faulty drivers can cause the IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error. To fix this issue, you can check for driver updates in Device Manager or download the latest drivers from the manufacturer's website.
Step 1. Press the Windows key + X and select "Device Manager".
Step 2. Expand the device category that has a yellow exclamation mark next to it.
Step 3. Right-click on the device and select "Update driver".
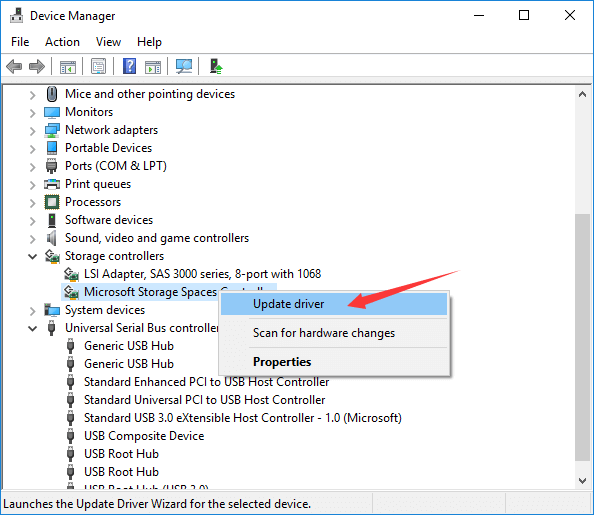
Step 4. Follow the on-screen instructions to install the latest drivers.
Alternatively, you can download the latest drivers from the manufacturer's website and install them manually.
Checker (SFC) scan System File Checker is a tool that scans for and repairs corrupt system files. To run an SFC scan, follow these steps:
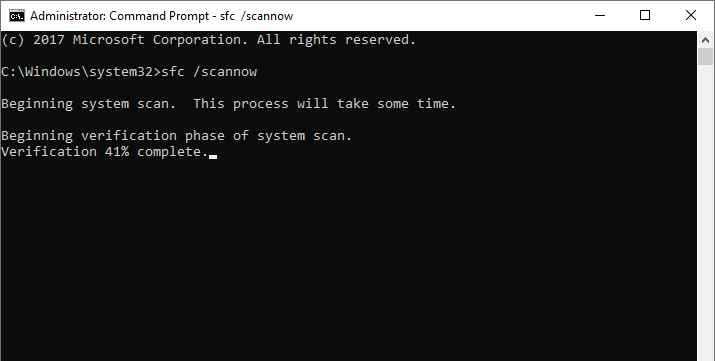
Step 1. Press the Windows key + X and select "Command Prompt (Admin)".
Step 2. Type sfc /scannow and press Enter.
Step 3. Wait for the scan to complete.
Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) is a tool that repairs corrupt system images. To run a DISM scan, follow these steps:
Step 1. Press the Windows key + X and select "Command Prompt (Admin)".
Step 2. Type "DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth" (without quotes) and press Enter.
Step 3. Wait for the scan to complete.
Malware can cause the irql not less or equal error. Run a malware scan using Windows Defender or any other reputable antivirus software.
Step 1. Press the Windows key + I to open the Settings app.
Step 2. Click on Update & Security > Windows Security > Virus & threat protection > Scan options.
Step 3. Select the type of scan you want to run (Quick scan, Full scan, or Custom scan).
Step 4. Click on "Scan now" to start the scan.

If your hard drive has developed bad sectors or suffers from file system corruption, it can cause system instability and blue screen errors like IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL. This is especially true if the error occurs during startup, system load, or when accessing large files.
Note: If the disk has a large number of bad sectors or the repair fails, it's best to replace the drive. Continuing to use a failing disk increases the risk of data corruption and system crashes.
Step 1. Download, install, and launch DiskGenius Free Edition .
Step 2. Select the suspected drive from the left panel. Click Tools > Verify or Repair Bad Sectors.
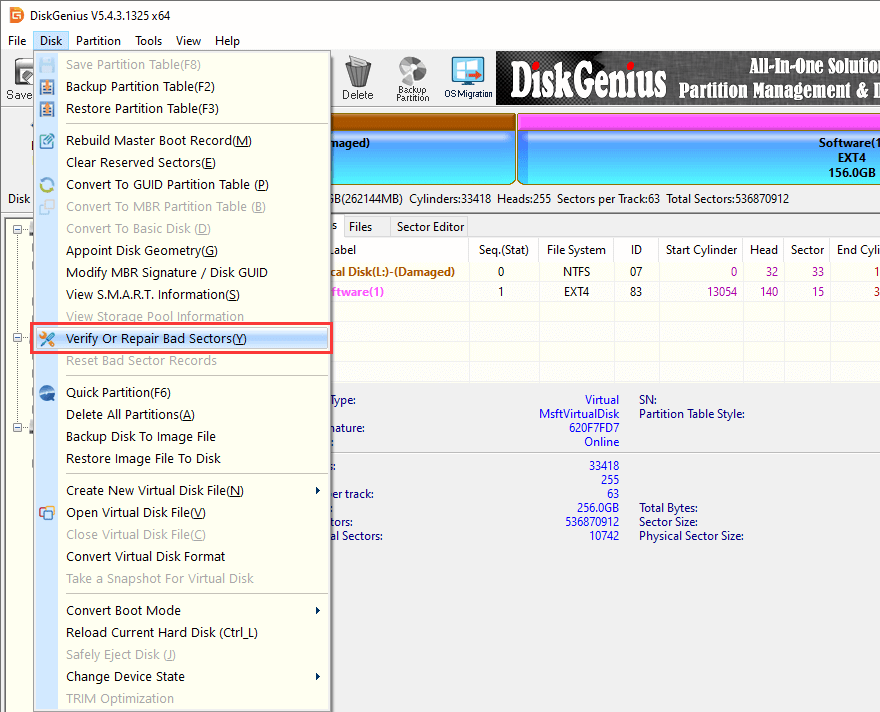
Step 3. Start the "Start Verify" button to check for physical damage
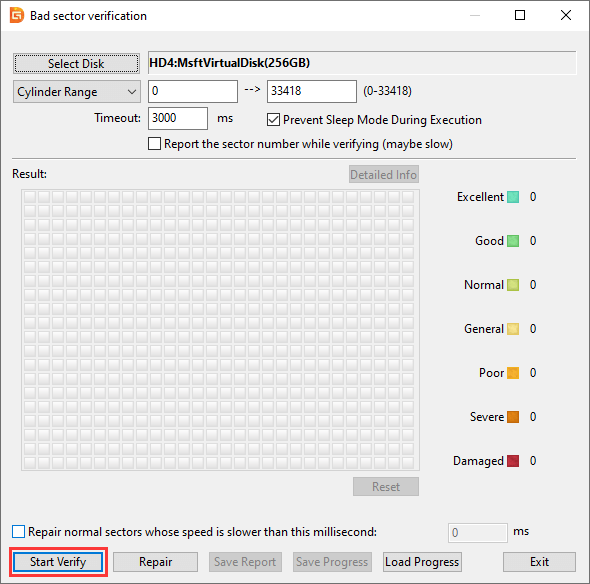
If bad sectors are found, you should back up files as soon as possible, after which you can try repairing bad sectors or consider replacing the drive.
Overclocking is running your CPU, GPU, or RAM over their factory-set limits. This might make your system unstable, especially if it isn't properly cooled or tuned. If you're getting blue screen problems that say "IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL," you should check to see if overclocking is on and turn it off.
Step 1. To get into BIOS/UEFI, restart your computer and press the right key (typically Del, F2, or Esc).
Step 2. Go to the Advanced, Performance, or Overclocking tab. This may be different for each model of motherboard.
Step 3. Look for settings that say "CPU Ratio", "XMP", "Turbo Boost", or something like that.
Step 4. Turn off or set to default or auto any options that have anything do with overclocking.
Step 5. Press F10 and confirm to save your modifications and leave BIOS.
After restarting, see if the system is more stable. If the blue screen errors stop, it's likely that overclocking was part of the problem.
When you look at a BSOD produced by IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL, you might see that the crash dump leads to ntoskrnl.exe. This can be hard to understand, especially if you think the Windows kernel is broken.
ntoskrnl.exe is not always the real problem; it's just where the crash happened when a deeper problem came up. This system file manages memory, drivers, and hardware abstraction. When a driver does anything wrong, such trying to access memory that isn't there, the kernel catches the error and shows the blue screen.
If you've already gone through the 11 solutions above and still experience crashes involving ntoskrnl.exe, here are additional methods specifically targeting this issue:
Sometimes, a recent driver update, especially one for graphics or the network, might make things unstable, which can cause IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL BSODs with ntoskrnl.exe.
Step 1. Press Windows + X and choose Device Manager from the list.
Step 2. Open the area (such Display adapters, Network adapters, or any other ones you just modified).
Step 3. Right-click the device and choose Properties.
Step 4. If you can, click Roll Back Driver on the Driver tab.
Step 5. Follow the instructions on the screen and restart your computer.
Tip: If the rollback option is greyed out, try removing the driver and then downloading an older version from the manufacturer's website.
When the memory dump simply displays ntoskrnl.exe, it usually suggests that there is a problem with a driver that goes deeper. Driver Verifier makes drivers work under severe conditions to find the bad one.
Step 1. Press Windows + R, type "verifier", and hit Enter.
Step 2. Choose "Create custom settings (for code developers)", and then click Next.
Step 3. Look for choices like "Special pool" "Pool tracking" "Force IRQL checking" and "DDI compliance checking".
Step 4. Click Next, then pick "Select driver names from a list".

Step 5. Check all drivers that aren't from Microsoft, click Finish, and then restart your computer.
If you see a BSOD, look at the stop code or the new dump file to find out the name of the driver.
Tip: To turn off Verifier, start your computer in Safe Mode, open Command Prompt, and type verifier /reset.
If you change the BIOS settings in a way that makes the system unstable or crashes at the kernel level, including overclocking the RAM, setting custom voltages, or using aggressive CPU features, it can happen.
Step 1. Restart your computer and go into BIOS/UEFI (typically by pressing Del, F2, or Esc when it starts up).
Step 2. Find a menu item that says "Load Optimized Defaults" or "Restore Default Settings".
Step 3. Then, click "Save & Exit" to confirm the action.
Step 4. Start Windows and watch how the system works.
If the BSOD always points to ntoskrnl.exe, you can use a program like WinDbg or BlueScreenView to look at the crash dump file and find the driver that is causing the problem.
Step 1. Press Windows + R, type %SystemRoot%\Minidump, and hit Enter.
Step 2. Get BlueScreenView or WinDbg Preview from the Microsoft Store and install it.

Step 3. Open the dump file and look under the "Caused by driver" or "call stack" part.
Step 4. Find the name of the bad driver (such nvlddmkm.sys or rtwlane.sys) and either look it up or change it or uninstall it.
If your BIOS or chipset drivers are out of date, they may not work with new hardware or Windows upgrades, which can cause low-level problems.
Step 1. Go to the support page for your motherboard maker. Find the most recent BIOS version and chipset driver that works with your model.
Step 2. Follow the vendor's BIOS update documentation very carefully. You may need a USB flash drive or a built-in update software.
Step 3. Install the chipset drivers in Windows and then restart.
Be aware that updating the BIOS can be risky. Check that your PC is getting stable power and follow the prescribed steps carefully.
If none of these solutions work, you may need to consider a system restore or resetting your PC to its factory settings. If the issue persists, contact a professional technician or Microsoft support for further assistance.
Booting your computer from a USB flash drive can be useful when you need to install a new operating system, perform a system repair, or run a virus scan. Here are the steps to create a bootable USB flash drive and boot computer from it:
Step 1. Insert the USB flash drive into an available USB port on a working computer running Windows 10 or 11.
Step 2. Install and run DiskGenius Free Edition on this computer. Select the USB drive which will be created as a bootable disk, then click "Tools" – "Create WinPE Bootable USB Drive of DiskGenius".
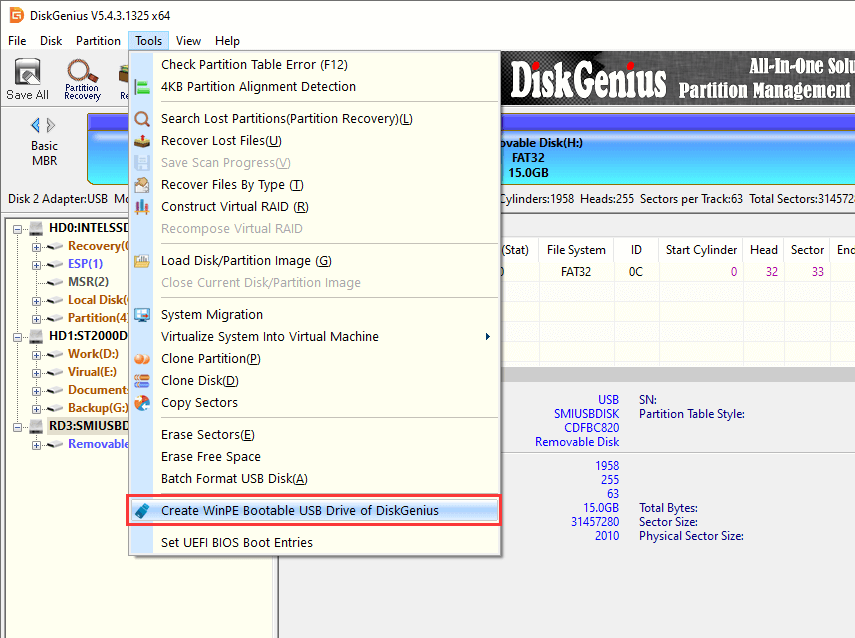
Step 3. Click the "OK" button on the pop-up window.
Step 4. Wait for a couple of seconds, and the bootable USB disk will be created successfully.
Step 5. Eject the USB flash drive. Once the bootable files have been copied onto the USB flash drive, safely remove it from your computer.
Your bootable USB flash drive is now ready to use. You can insert it into a computer and boot from it by following the steps outlined in Part 2.
Step 1. Insert the USB flash drive into an available USB port on the unbootable computer.
Step 2. Restart your computer, and immediately begin pressing the appropriate key to access the boot menu. This key varies by manufacturer but it is typically F2, F12, ESC, or Del. Check your computer's manual or look for on-screen instructions during startup .
Step 3. Once you access the boot menu, use the arrow keys to highlight the option for booting from a USB flash drive and press Enter. Save changes and exit BIOS.
Step 4. Your computer will restart on its own and then boot from the USB flash drive.
Once your computer has booted from the USB flash drive, DiskGenius will be launched automatically. If you want to access Command Prompt, click the Start menu to locate it.
1. What is IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL in Windows 2000?
It is a blue screen of death (BSOD) error message that can occur in Windows 2000. It typically indicates that there is a problem with a driver or hardware device that is causing an interrupt request level (IRQL) that is higher than it should be.
2. What is Irql_not_less_or_equal after changing RAM?
It is a common Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) error message in Windows, and it indicates that there is a problem with a driver or hardware. When this error occurs after changing RAM, it could mean that the new RAM is either faulty or incompatible with your system.
3. Can SSD cause IRQL not less or equal?
Yes, an SSD (Solid State Drive) can potentially cause the IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error to occur on a Windows system. However, it is less common than some of the other causes of this error.
One possible cause of the error is a faulty SSD driver. If the driver for your SSD is outdated, incompatible, or corrupted, it can cause this error to occur. You can check for driver updates through Device Manager or the manufacturer's website.
Another potential issue with an SSD is firmware problems. If the firmware on your SSD is outdated or corrupted, it can cause the IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error to occur. You can check for firmware updates on the manufacturer's website.
It is also possible that the SSD itself may be faulty or failing, which can cause this error. You can check the health of your SSD using diagnostic software provided by the manufacturer.
In summary, while an SSD can cause the IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error to occur, it is less common than other causes such as faulty hardware or outdated drivers. If you suspect that your SSD is causing this error, you can try updating the driver or firmware, or running diagnostics to check for hardware issues.
4. How do I stop IRQL less or equal in Windows 10?
There are several steps you can take to try to stop the IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error from occurring in Windows 10. Here are some possible solutions: update your drivers, check if the RAM works well, run a system scan, check for malware, or restore OS to a previous state.
5. Can overheating cause IRQL not less or equal?
Yes, overheating can cause the IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error to occur on a Windows system. When a computer's CPU or graphics card overheats, it can cause instability in the system, leading to the error message. Overheating can also cause other problems, such as system crashes, freezes, and slowdowns.
When a computer overheats, the cooling system may not be able to keep up with the heat generated by the CPU or graphics card. This can cause the components to become unstable, leading to crashes and errors such as IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL.
To prevent overheating, it is important to ensure that your computer's cooling system is functioning correctly. You can clean the fans and vents of dust and debris, ensure that there is adequate airflow around the computer, and check that the cooling system is working correctly. If you are still experiencing the error message after addressing potential overheating issues, it may be necessary to seek professional help to diagnose and fix the issue.
6. What causes a corrupted graphics driver?
A corrupted graphics driver can be caused by a variety of factors, including, installation errors, malware or virus infection, power failure, outdated driver, overclocking, hardware issues, and Windows system updates. It is important to keep your graphics driver up-to-date to prevent compatibility issues and other problems. If you suspect that your graphics driver is corrupted, you can try updating the driver or reinstalling it to fix the issue.
7. How do I know if my Windows 10 driver is corrupted?
If you suspect that a driver on your Windows 10 system is corrupted, you can look for some common signs that indicate that the driver is not working correctly. Here are some symptoms to look for:
8. What is IRQL that is too high?
The "IRQL that is too high" error message is less common and can occur when a device or driver is trying to access a lower IRQL level than it is permitted to access. This can happen when a device or driver is not properly configured or when there are conflicts between different devices or drivers. The "IRQL that is too high" error can cause system instability, crashes, and other issues. If you are experiencing this error message, it is recommended to troubleshoot your system and identify the underlying cause of the error, which could be due to faulty or outdated drivers, conflicts between devices or drivers, or other software-related problems.
10. Is IRQL not less or equal a virus?
No, "IRQL not less or equal" is not a virus. It is actually a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) error message that is caused by a software or hardware issue on your computer. The error message usually indicates that a driver has tried to access a memory address that it is not allowed to access, which can cause system instability and crashes.
While there are some viruses and malware that can cause BSOD errors, "IRQL not less or equal" is not specifically associated with any virus or malware. If you are experiencing this error message, it is recommended to troubleshoot your system and identify the underlying cause of the error, which could be due to a faulty driver, a hardware issue, or other software-related problems.
11. How do I fix infinite blue screen recovery on Windows 10/11?
An infinite blue screen on Windows 10 or 11 can be caused by a variety of reasons, including hardware failure, driver issues, software conflicts, or even malware infections. Here are some steps you can take to troubleshoot and fix the issue: restart computer, boot into Safe Mode, install Windows updates, run a malware scan, check hardware components, update drivers, restore system to a previous point.
12. How do I stop Windows 10 from collecting error info?
Windows 10 collects error information to help diagnose and fix problems that occur on your system. Once you've disabled the Windows Error Reporting Service, Windows will no longer collect error information from your system. Note that this may make it more difficult to diagnose and fix problems on your system, so it's not recommended unless you have a specific reason for disabling error reporting. If you don't want to share this data with Microsoft, you can disable error reporting by following these steps:
Step 1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box. Type "services.msc" and press Enter to open the Services app.
Step 2. Scroll down the list of services until you find "Windows Error Reporting Service".
Step 3. Right-click on the service and select "Properties". In the "Windows Error Reporting Service Properties" dialog box, set the "Startup type" to "Disabled". Click "Apply" and then "OK" to save the changes.
13. How do I disable unnecessary drivers in Windows 10?
Note that disabling drivers can sometimes cause issues with your system, so it's important to only disable drivers that you know are unnecessary or causing problems. If you're unsure about a particular driver, it's best to leave it enabled. To disable unnecessary drivers in Windows 10, follow these steps:
Step 1. Open the Device Manager by pressing the Windows key + X and selecting "Device Manager" from the menu that appears.
Step 2. In the Device Manager, locate the device driver that you want to disable. Right-click on the driver and select "Disable device" from the context menu. Alternatively, you can also select "Uninstall device" to completely remove the driver from your system.
Step 3. In the confirmation dialog box, click "Yes" to confirm the action. Repeat steps 2-4 for any other drivers that you want to disable.
DiskGenius - Free disk partitioning software for Windows PCs and servers to extend partitions, partition hard drives, format SSDs, clone SD cards, wipe hard drive data, and more.

DiskGenius is a one-stop solution to recover lost data, manage partitions, and back up data in Windows.
Download